What is multi-access edge computing?
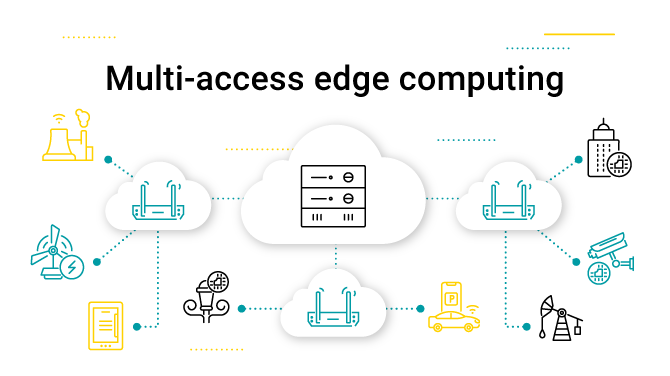
Network architecture is evolving. Today, developments allow for smarter and more efficient ways to deliver computing power and data storage. A newer concept gaining traction is multi-access edge computing.
But what is it and how does it relate to edge computing? This blog post explores the relationship between both concepts and how multi-access edge computing or MEC can be used to improve network resource utilization.
What is multi-access edge computing?
Multi-access edge computing is considered the natural progression of computing and data processing. In typical network environments, assets like servers are often based in various locations, and with cloud computing, that often means far from network infrastructure that produces data.
MEC is a standard architecture organizations use. It allows networks to better process data, driving efficiency. Cloud-based IT service environments that were once far away are now closer to data-producing devices. And a most notable win is that real-time data processing can happen at lower latency, making it easier to transfer and process more data faster.
Multi-access edge computing vs edge computing
What about edge computing? Edge computing is considered a concept used to describe how networks are improved by bringing resources to the "edge of the network". Multi-access edge computing is a collection of standards designed to help organizations deliver edge computing capabilities. 
As a concept, edge computing has gained ground, however, MEC standards are still taking shape. Today, fundamental MEC standards span framework and reference architecture. This area relates to functional elements, the reference points between them, and a number of MEC services (think platforms and applications operating in a network).
How does multi-access edge computing work?
Multi-access edge computing is meant to improve network efficiency. For example, a network includes a user image analysis application. The application communicates with the core network that’s connected to a backend server that hosts an image analysis service.
On an average day, a user accesses the image application and sends a request through the core network and to the backend server that performs the image analysis and returns a result. Latency, in this example, could be 100ms. If the needs of the user evolve to include live video capture, latency could become a challenge. Live video is resource-intensive given video quality and the need for real-time data transfer.
Edge computing solves the problem by bringing edge servers closer to the image analysis application. In a case where edge servers are not located near the image application, MEC is ideal. A radio access network installed at the data centre of the network or the base station decreases latency considerably. The radio access network also lessens the load on the backend server, freeing it to be repurposed for other tasks.

5G also presents an exciting opportunity for MEC-enabled networks. The speed at which data is transferred on a 5G network means faster communication and larger amounts of data transmission in less time.
Benefits of multi-access edge computing
These are better described as benefits of edge computing as edge computing is an overarching term that MEC is a component of.
Benefits include:
Decreased latency
Edge computing architecture enables faster data transfer. As more services are brought to the edge of a network, they can operate faster for organizations. Organizations are able to leverage real time insights to proactively monitor IoT hardware and preempt potential outages before they cause large operational setbacks.
Greater security and reliability
As the cloud expands, the conversation around security deepens. Edge computing offers some reprieve for concerned security specialists. The nature of edge computing involves spreading more data across a network. This may seem like risky business, but it offers organizations greater resilience. Hackers stand a better chance of causing more damage to a network without edge computing capabilities using a DDoS attack, than intercepting a piece of data from a service on the edge.
Edge computing services are also often provided by cloud hyperscalers such as Amazon’s AWS or Microsoft’s Azure. These services are state of the art, receive billions in investment, and are constantly monitored for threats. They are also designed and updated to meet compliance requirements as they are released.
Scalability and savings
Edge computing gives organizations the chance to scale faster. Without the need for high CapEx costs, organizations can scale or dial back on services where computing requirements change.

Multi-access edge computing and device management
IoT device management is another area MEC-enabled organizations can win. IoT devices are low-energy and low-processing power devices. Bringing services to the edge of the network allows an enterprise to leverage network resources, pushing data to servers for analysis. IoT devices also need to be managed, and this is where solutions like Coiote IoT Device Management are essential.
Coiote IoT Device Management in action
Coiote IoT DM makes it possible to deploy new IoT solutions in a highly scalable way. In multi-access edge computing environments, this means less load on infrastructure without compromising control and device management.
In a manufacturing plant, multi-access edge computing and Coiote IoT Device Management can provide a more streamlined operation. Where a multi-access edge computing server is able to process analytical data on sensors, tracking anything from operating temperatures to proximity of workers to improve safety, Coiote IoT Device Management helps the plant control each sensor. Through reporting on individual sensors, plant managers can ensure continuous production, avoiding operational challenges that may arise before they become complex or critical issues that lead to plant downtime.
Summary
Multi-access edge computing offers organizations a chance to enhance network capabilities. By bringing more services to the edge of the network, enterprises can speed up data transfer, and free up existing hardware to perform other important tasks. Wins for MEC-enabled networks include increased speed and lower latency, better security and reliability, and stability, as well as cost savings. In networks where IoT devices must be managed efficiently, Coiote IoT DM offers organizations greater scalability, security, speed, and a simpler view of their IoT ecosystem.
Recommended posts
- How can you effectively tackle the challenges of IoT development?
- IoT communication protocols explained [with measurements for NB-IoT]
- How to Streamline Data Handling with LwM2M Solutions?
Subscribe to stay in the loop with all our latest content:
Recommended posts

![IoT communication protocols [with measurements for NB-IoT]](/media/avssite/news/Communication-Protocols-Comparison_cover_new.png)
